UNIT 10
Last unit!!!! :)
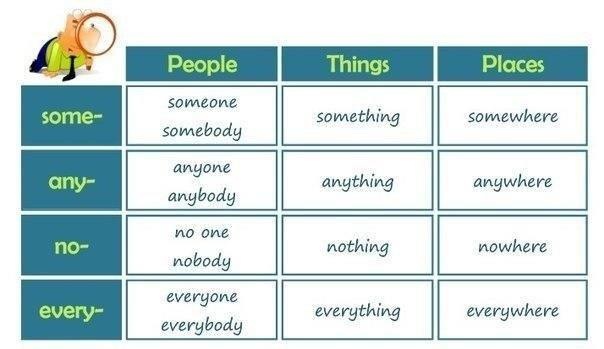
Online activities:
www.agendaweb.org/grammar/anybody-someone-indefinite-pronouns-exercises.html
UNIT 11 & 12
PASSIVE VOICE - PRESENT SIMPLE:
Passive: The flowers are watered by the gardener every evening.
PASSIVE VOICE - PAST SIMPLE:
Passive: The flowers were watered by the gardener every evening.
ACTIVITIES:
www.ego4u.com/en/cram-up/grammar/passive/exercises?simple-past
www.englisch-hilfen.de/en/exercises/active_passive/sentences_simple_past.htm
www.perfect-english-grammar.com/passive-exercise-2.html
UNIT 8
if + present simple, ... will + infinitive
It's used to talk about things which might happen in the future. Of course, we can't know what will happen in the future, but this describes possible things, which could easily come true.
- If it rains, I won't go to the park.
- If I study today, I'll go to the party tonight.
- If I have enough money, I'll buy some new shoes.
UNIT 7
| Tense | Direct Speech | Reported Speech |
|---|---|---|
| present simple | I like ice cream | She said (that) she liked ice cream. |
| present continuous | I am living in London | She said (that) she was living in London. |
ONLINE ACTIVITIES:
www.perfect-english-grammar.com/reported-speech-exercise-12.html
www.perfect-english-grammar.com/reported-speech-exercise-10.html
UNIT 6
Along this unit we are going to study another type of future form:
BE GOING TO
USES: plans and intentions.
FORM:
Sj + am/is/are + going to + infinitive verb.
E.g. I am going to play tennis next Saturday.
Online resources
www.agendaweb.org/verbs/future-be-going-to-exercises.html
UNIT 5
- It will snow tomorrow, it is so cold.
- I'm very thirsty. I will drink a glass of water.
- We are leaving at two o'clock.
THANKS GIVING DAY
UNIT 4
PAST CONTINUOUS
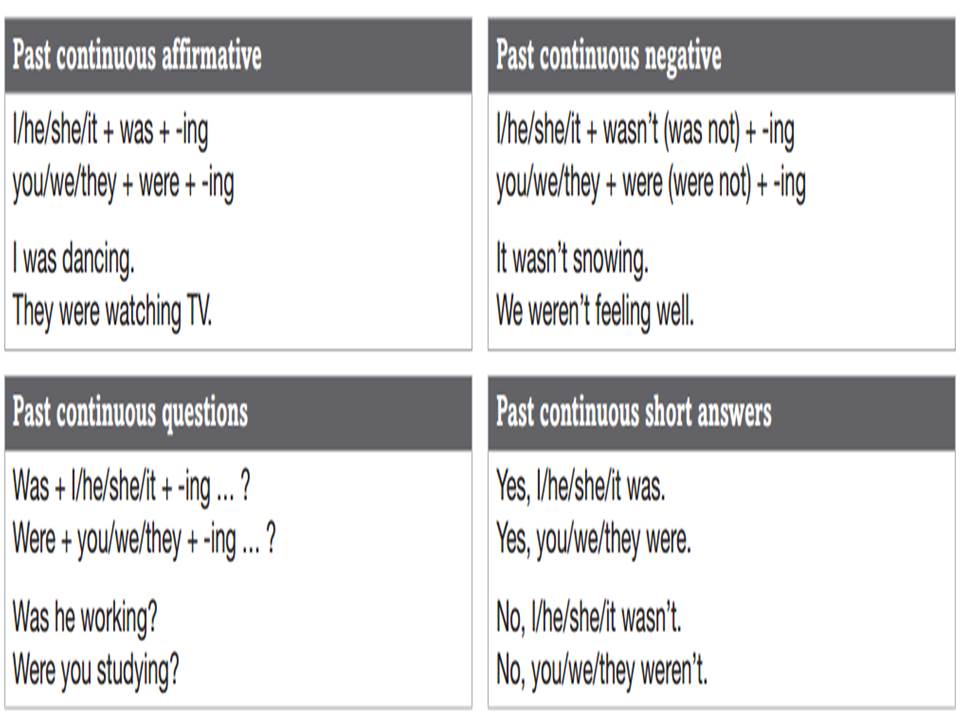
UNIT 3
Along this unit we are going to estudy the comparative and superlative form and "too" / "enough".
COMPARATIVE
1. EQUALITY:
Form: (not) as + adj + as = tan… como
Ex.
My sister is as intelligent as him.
He is not as tall as Gasol.
2. INFERIORITY:
Form: less + adj + than = menos… que
Ex.
He is less tall than Gasol.
3. SUPERIORITY:
Form:
a) Short adjectives: adj-er + than
Ex. He is taller than Gasol.
b) Long adjectives: more + adj + than
Ex. The exam is more difficult than the last one.
SUPERLATIVE
a) Short adjectives:
Form: the + adjective-est + (noun) + (in /of) = el /la más...
Ex. Jack is the tallest of the class.
b) Long adjectives:
Form: the most + adjective + (noun) + (in /of) = el / la más...
Ex. She is the most beautiful girl I’ve ever seen.
SPECIAL RULES
1. Adjectives that finish in consonant + vowel + consonant: you have to double the las consonant. Ex:
Big - bigger - the biggest
Thin - thinner - the thinnest
2. Adjectives that finish in Y → ier /iest. Ex:
Easy - easier - the easiest
Pretty - prettier - the prettiest
3. Adjectives that finish in E → r /st. Ex:
Nice - nicer the – nicest
Large - larger - the largest
IRREGULAR FORMS
Good - better - the best
Bad - worse - The worst
Far - farther /further - the farthest /furthest
ONLINE EXERCISES:
Comparatives:
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/adjectives.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/adjectives2.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/comparativeadjectives.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/comparativeadjectives2.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/comparativeadjectives3.html
Superlatives:
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/superlativeadjectives.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/superlativeadjectives2.html
Comparative and superlative:
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/superlativecomparative.html
www.learnenglish-online.com/grammar/tests/superlativecomparative2.html
TOO / ENOUGH
TOO
Uses: Too goes before adjectives and adverbs. It has a negative meaning and shows that something is more than enough, more than necessary or more than wanted.
Form: too + adjective/adverb + to –infinitive. *
Ex: Helen is too rude to become a doctor.
ENOUGH
Uses: Enough goes before nouns but after adjectives or adverbs. It has positive meanings and shows that there is as much of something as is wanted or needed.
Form: Adjective/adverb + enough + to –infinitive
Ex: The weather is warm enough to swim.
ONLINE EXERCISES
UNIT 2
UNIT 1
VERB TO HAVE in present
![]() I have
I have
You have
![]() He has
He has
She has
It has
![]() We have
We have
You have
They have
PRESENT PERFECT
USES:
When an action was completed (finished) at some point in the past.
When the action extends to the present. Ex.
“I have walked two miles already [but I'm still walking].”
“I have run the Boston Marathon [but that was some time ago].”
You CANNOT use the Present Perfect with specific time expressions such as: yesterday, one year ago, last week…
We CAN use the Present Perfect with unspecific expressions such as: ever, never, once, many times, several times, before, so far, already, yet, etc.
FORM:
Affirmative:
SJ + HAVE/HAS + PAST PARTICIPLE
“I have been in London.”
“She has gone to Paris.”
Negative:
SJ + HAVE/HAS + NOT + PAST PARTICIPLE
“I have not (or haven’t) been in London.”
“She has not (or hasn’t) gone to Paris.”
Interrogative:
HAVE / HAS + SJ + PAST PARTICIPLE?
“Have you been in London?”
“Has she been in London?”
ONLINE ACTIVITIES:
www.ego4u.com/en/cram-up/tests/present-perfect-simple-1
English Revision
Oh, I can't remeber anything! No worries...
VERB "TO BE" PRESENT SIMPLE"

VERB "TO HAVE" PRESENT SIMPLE
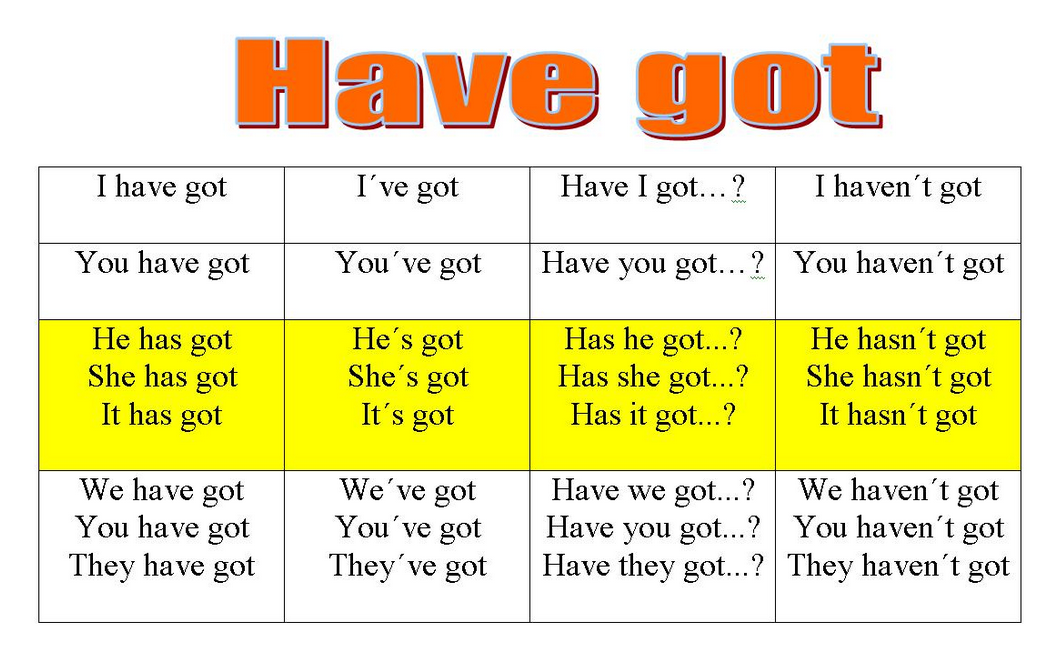
PRESENT SIMPLE
PRESENT SIMPLE
PAST SIMPLE
.jpg?ph=f6c3739523)