SOCIAL SCIENCE - UNIT 6


CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 6 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales. Esta unidad tiene por título Early Modern Spain (“España en la Edad Moderna”), y en ella aprenderá:
- El reinado de los Reyes Católicos. La cuestión sucesoria, el tribunal de la Santa Inquisición y el descubrimiento de América.
- Los grandes conquistadores, navegantes y exploradores. Los viajes de Colón, Hernán Cortés, Francisco Pizarro, Fernando Magallanes y Juan Sebastián Elcano.
- El reinado de los Habsburgo. Los hechos importantes del reinado de Carlos I y Felipe II y fin de la dinastía.
- Los escritores y pintores más relevantes del Siglo de Oro español.
- Los Borbones en España. El reinado de Felipe V. El reinado de Carlos III y la modernización y embellecimiento de Madrid.
- El estudio de un personaje histórico y la biografía.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando las audiciones de la unidad y la presentación powerpoint ubicadas en la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a pensar con vuestros hijos en personas de nuestro entorno que provengan de otros países. Podéis explicarles que, en aquellos casos en que su lengua materna sea el español, se deberá a que en su momento sus pueblos formaban parte de los territorios españoles y, por ello, ambas tradiciones y culturas se fusionaron y conservaron el idioma hasta hoy aunque con algunas diferencias puntuales. Se puede localizar en un mapa algunos de estas regiones.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
VOCABULARIO
Early Modern Spain (España en la Edad Moderna)
absolute power = poder absoluto
advance = avance
Age of Discovery = Época de los Descubrimientos
arrest = detener
Aztecs = Los Aztecas
Botanical Gardens = El Jardín Botánico
Bourbons = Borbones
canals = canales
Canary Islands = Islas Canarias
captive = cautivo
Caribbean = Caribe
Catholic Monarchs = Los Reyes Católicos
Christopher Columbus = Cristóbal Colón
colonise = colonizar
commoners = plebeyo
conquistadors = conquistadores
contribution = contribución
court = corte
disagree about = discrepar, estar en desacuerdo
Discovery of America = el Descubrimiento de America
distant places = lugares lejanos
dynasty = dinastía
Early Modern Age = Edad Moderna
economic crisis = crisis económica
eldest child = primogénito, primer hijo
empire = imperio
event = acontecimiento
expedition = expedición
expel = expulsar
explorer = explorador
face = afrontar
family tree = árbol genealógico
fight a war against = estar en guerra con
fountain = fuente
French Revolution = La Revolución Francesa
Golden Age = El Siglo de Oro
grandson = nieto
Hapsburgs = Los Habsburgo
heir = heredero
Immaculate Conception = La Inmaculada Concepción
imprison = encarcelar, recluir
improve = desarrollar
Incas = Los Incas
increase = incrementar, aumentar
institutions = instituciones
interrogate = interrogar
intolerant = intolerante
invention = invento
leech = sanguijuela
monument = monumento
Museum of Natural History = El Museo de Historia Natural
natives = aborígenes
New Spain = La Nueva España
novel = novela
painter = pintor
peoples = pueblos, poblaciones
play = obra de teatro
poem = poema
possessions = territorios, posesiones
Prado Museum = Museo del Prado
privileges = privilegios
religious unity = unificación religiosa
road system = red vial, red de carreteras
Royal Academies = Las Reales Academias
Royal Astronomical Observatory = El Real Observatorio Astronómico
Royal family = LA Familia Real
Royal Palace = Palacio Real
sail across = cruzar en barco (navegar)
shopkeepers = tenderos
short story = relato
slaves = esclavos
Spanish Inquisition = La Inquisición
spies = espías
state = estado
supporter = defensor, partidario
timeline = eje cronológico
torture = torturar
unite = unificar
view = vista
voyage = viaje
voyage of discovery = viaje de descubrimiento
War of the Spanish Succession = la Guerra de Sucesión Española
Western route = ruta occidental (por el oeste)
writer = escritor
REVIEW:
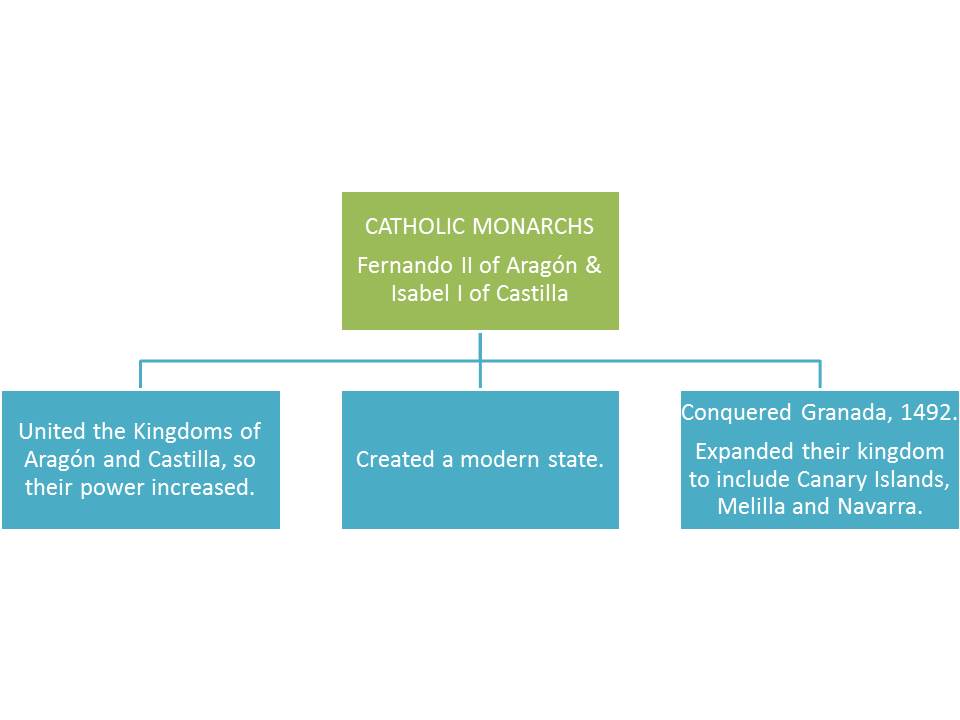
CATHOLIC MONARCHS:
- Isabel of Castilla and Fernando of Aragón married in 1469.
- Isabel’s brother Enrique was King of Castilla. When he died Isabel declared queen, but the daughter of Enrique, Juana wanted to be the queen too. There was a war and Isabel won in 1479, when Fernando became King of Aragón.
Things that they did:
- United the Kingdoms of Castilla and Aragón, so they increased their power.
- Created a modern state.
- Conquered Granada, 1492.
- Included Canary Islands, Melilla and Navarra to their kingdom.
- Gave money to Christopher Columbus for a voyage of discovery.
- Established Inquisition, 1478, an organization with special powers to find people who didn’t follow Catholic religion.
- Expelled Jewish people from their kingdom, 1492.
CONQUISTADORS:
- Christopher Columbus: 1492, discovered America. He arrived to San Salvador and Hispaniola.
- Hernán Cortés: 1519, went to Mexico. He became the governor of New Spain.
- Francisco Pizarro: 1532, went to Peru. He became the governor of Peru.
*Fernando Magallanes: was the first to sail across the Pacific Ocean.
*Juan Sebastián Elcano: first person to sail around the world (1519-1522).
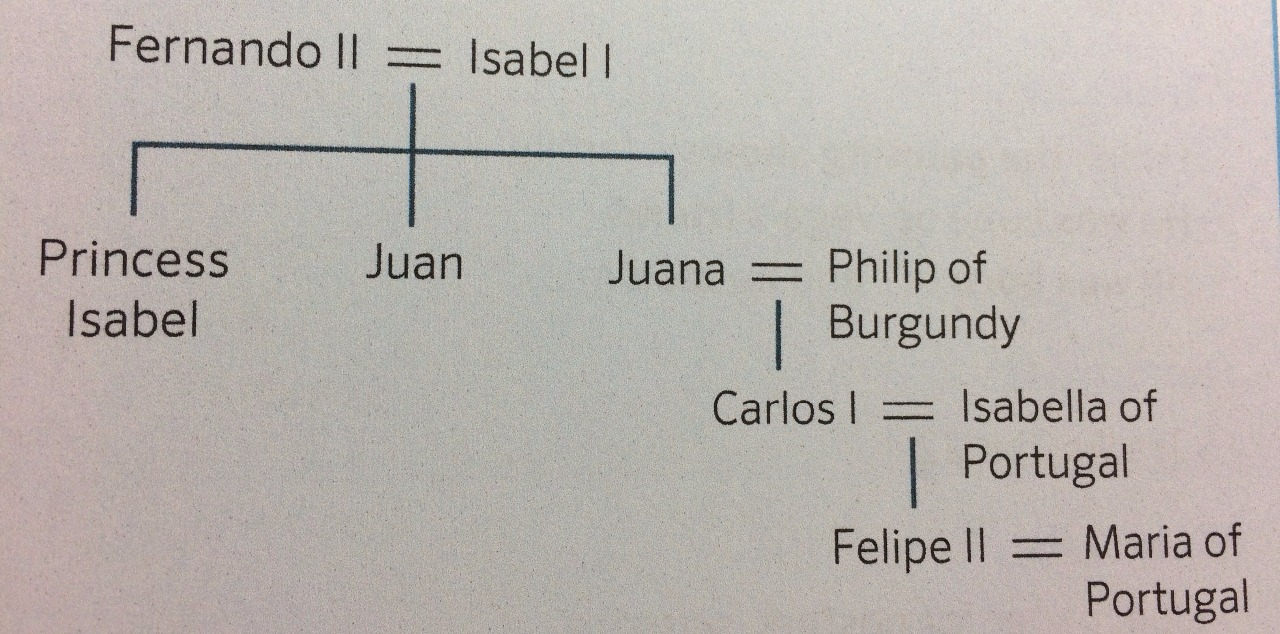
HAPSBURGS:
- Hapsburgs ruled Spain during 16th and 17th centuries.
- Fernando and Isabel had five children: Isabel, Juan, Juana, María and Catalina. Juan was their heir, but he died as her sister Isabel. Then the son of Isabel also died, so Juana became the heir. She was married with Philip of Burgundy, who was a Hapsburg. They had a son, Carlos.
- Juana became queen when her mum Isabel died, but her husband and her dad ruled for her. After the death of Fernando, her son became King Carlos I of Castilla and Aragón.
Dynasty: Carlos I – Felipe II – Felipe III – Felipe IV – Carlos II
End of dynasty:
- Many economic problems.
- Wars agains other countries.
- Spain lost some parts of its lands in Europe.
- Carlos II died in 1700 without any children.
BOURBONS:
After the death of Carlos II other European countries disagreed about who should be the next king, so the War of the Spanish Succession started. As a result, Spain lost power and lands in Europe and Bourbons ruled the country.
Felipe V:
- Was the first king, he ruled with absolute power the first half of 18th century.
- Centralized the government.
- Divided Spain in provinces.
Carlos III:
- King during the second half of 18th century.
- Modernised the country, built road systems and canals.
- Created new institutions in Spain: Royal Academies, Museum of Natural History.
- Made cities more modern and beautiful.
SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 5



CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 5 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales Oxford Think Do! Learn 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Spain in the Middle Ages (“España en la Edad Media”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La España visigoda: La llegada de los visigodos y el reino visigodo de Toledo. El rey Recaredo y el Concilio de Toledo.
- Las huellas de la cultura en la España visigoda.
- Los árabes en España: La Batalla de Guadalete (año 711). Al-Ándalus: sistema político, territorial y la vida cotidiana.
- La Reconquista: la resistencia de Don Pelayo y la Batalla de Covadonga. Los Reinos Cristianos: Sistema político (la monarquía), política exterior, la vida cotidiana.
- El origen Camino de Santiago.
- Las gestas y personajes de la Reconquista: El Cid Campeador.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando las actividades de Let’s play! ubicados la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a localizar en un mapa de España los distintos lugares que se mencionan en la lección y a comparar la actual organización política de la Península Ibérica con aquella que existía en la Edad Media (La Reconquista y los Reinos Cristianos y al-Ándalus).
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina.
VOCABULARIO:
Spain in the Middle Ages (España en la Edad Media)
achievements = logros
al-Andalus = al-Ándalus
Allah = Alá
Arabian Peninsula = Península Arábiga
Arabic = idioma árabe
army = ejército
authority = autoridad
badge = emblema
Battle of Covadonga = Batalla de Covadonga
Battle of Guadalete = Batalla de Guadalete
Battle of Navas de Tolosa = Batalla de las Navas de Tolosa
belief = convicción, creencia
bishop = obispo
Black Death = la Peste Bubónica (o Negra)
blacksmith = herrero
border = frontera
caliph = califa
caliphate = califato
cathedral = catedral
Catholicism = catolicismo
Christian = cristiano
clay = arcilla
clergy = clero
conquest = conquista
Córdoba Caliphate = el Califato de Córdoba
council = consejo
Council of Toledo = El Concilio de Toledo
customs = tradiciones o costumbres
decrease = disminuir
defeat = derrotar, vencer
emir = emir
emirate = emirate
equal = igual
expand = extenderse
follower = seguidor, fiel
fortress = fortaleza
Germanic tribe = tribu germánica
governor = gobernador
Great mosque = mezquita mayor
irrigated farming = agricultura de regadío
Islam = el Islám
Jewish = judío
King Recaredo = el rey Recaredo
Koran = El Corán
laws = leyes, legislación
leather goods = objetos de piel
legend = leyenda, gesta
lord = señor (feudal)
merchant = mercader, comerciante
miller = molinero
Mozarab = mozárabe
Muslim = musulmán
Ostrogoths = ostrogodos
pattern = filigrana
pilgrimage = peregrinación
pottery = cerámica
prophet = profeta
raise = criar
reconquer = reconquistar
rights = derechos
Roman laws = derecho romano
route = itinerario, ruta
rule = gobernar
running water = agua corriente
sacred = sagrado
souk = el zoco
Taifa kingdoms = Reinos de Taifas
taxes = impuestos
teachings = enseñanzas, doctrina
territory = territorios
thinker = pensador
treasure = tesoro
Visigoths = los visigodos
weapon = arma
wheat = trigo
REVIEW UNIT 5 SOCIAL SCIENCE
VISIGOTHS
· Important Germanic tribe. Arrive in 5th century.
· 507 A.D. establish the Kingdom of Toledo. Capital – Toledo.
Government:
· King made the laws.
· Council of Toledo – meetings of the king with nobles and bishops.
Culture:
· Spoke Latin.
· St. Isidoro of Sevilla was the first Christian to write an encyclopedia.
Religion:
· 589 A.D. King Recaredo converted to Catholicism.
Economy:
· Most were farmers so they live in the countryside.
· Population of cities decrease.
AL- ANDALUS
· 711 A.D. Muslim armies came from North-Africa. After the Battle of Guadalete, Muslims defeated Visigoths and al-Andalus became part of the Muslim empire, a caliphate ruled by a caliph. Al-Andalus was an emirate with the capital in Córdoba, governed by an emir who represented the caliph.
· 929 A.D. Abderramán III, declared al-Andalus an independent caliphate, called Córdoba Caliphate. Later on al-Andalus was divided into small taifa kingdoms.
Government:
· Cities were ruled by a governor who lived in the alcazaba.
Culture:
· Spoke Arabic.
· The mosque was an important building in the city for Muslims.
Religion:
· 7th century – Islam.
· God – Allah. Prophet – Mohammed. Sacred book – Koran.
Economy:
· Many merchants – gold, silk, leather goods and pottery. They bought and sold in the zouk.
· Farmers raised goats and sheep.
· They were experts in irrigated farming.
· Rice, wheat and oranges were introduced to Spain.
CHRISTIANS AND JEWISH IN AL-ANDALUS:
They could:
· Live were they wanted to.
· Practise their religion.
· Do any job.
· Be part of society and culture.
They had to:
· Pay special taxes.
· Wear a special bandage.
· Obey Muslims lows.
They couldn’t:
· Carry weapons.
· Have authority over a Muslim.
CHRISTIAN KINGDOMS
· 722 A.D. Battle of Covadonga, Don Pelayo (leader of Christians) defeated Muslims and he establishes the Kingdom of Asturias. Later on this became into Kingdom of León.
· There were other Christian kingdoms: Kingdoms of Castilla, Navarra and Aragón.
Government:
· King ruled the country.
· Lords ruled the small areas in which the kingdom was divided.
Culture:
· Each kingdom had a different language, but they came from Latin.
Religion:
· People were Christians.
· Priest and monks were important members of society. Monks lived in monasteries and copied and translated books.
Economy:
· Most were farmers; they produced what they needed, so there weren’t much trade.
· There were also artisans and soldiers.
Society:
· Was divided into: nobles, clergy and peasants.
RECONQUISTA
· 8th to 15th centuries, Christian kingdoms expanded to the south, they conquered al-Andalus.
Process:
1. 1085 A.D. Alfonso VI king of Castilla and León conquered Toledo.
2. 1212 A.D. Christians won the Battle of Navas de Tolosa in Jaén.
3. 1229 A.D. Jaime I King of Aragón conquered the Balearic Islands.
4. 1244 A.D. Jaime King of Aragón conquered parts of Valencia.
5. 1236 A.D. Fernando III King of Castilla and León conquered Córdoba.
6. 1248 A.D. Fernando III King of Castilla and León conquered Sevilla.
7. 1492 A.D. Christians conquered Granada.
NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 6
CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 6 de su libro de Ciencias Naturales Oxford Think Do Learn! 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Electricity and inventions (“La electricidad y los inventos”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La electricidad como forma de energía. Su formación: el átomo y sus partes.
- La carga eléctrica. La electricidad estática: sus efectos y sus usos.
- La corriente eléctrica. Conductores y aislantes eléctricos.
- La electricidad electromagnética.
- Los circuitos eléctricos. Los tipos de circuitos y sus componentes. La representación de un circuito eléctrico.
- Los usos de la energía eléctrica y su aplicación a las máquinas. Su importancia para la vida moderna.
- Tomás Edison y sus inventos. La bombilla, el quinetoscopio y el fonógrafo. La fundación del primer laboratorio científico.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos. Asimismo, os invito a investigar con vuestros hijos acerca de la actividad científica y la faceta de inventor de Edison. Se pueden usar enciclopedias o internet para conseguir cualquier tipo de información, por ejemplo, biografías, lista de inventos, dibujos o fotografías, videos, etc…
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
VOCABULARIO
String = cuerda.
Electric shock = descarga eléctrica.
Atom = átomo.
Electron = electrón.
Proton = protón.
Nucleus = núcleo.
Electric charge = carga eléctrica.
Static electricity = electricidad estática.
To rub = frotar.
Positively-charged = con carga positiva.
To repel = repeler.
Air pollution = contaminación del aire.
Factory = fábrica.
Dust = polvo.
Grid = red
Convection = convención.
Polystyrene = poliestireno.
Electric current = corriente eléctrica.
To flow = desplazarse, circular.
To plug = enchufar.
Socket = enchufe.
Switch = interruptor.
Wire = cable.
Eel = anguila.
Predator = depredador.
High voltage = alto voltaje.
Electrical conductor = conductor .
Painful = doloroso.
Magnetic field = campo magnético.
To wind = enrollar.
Coil = bobina, espiral.
Iron = hierro.
To squeeze = estrujar/exprimir.
Electric circuit = circuito eléctrico.
Loop = bucle, círculo.
Simple circuit = circuito sencillo.
Series circuit = circuito en serie.
Parallel circuit = circuito en paralelo.
To switch on = conectar.
To switch off = desconectar.
Power station = central (eléctrica).
Pylon = poste.
Fuse box = cuadro eléctrico.
Flood = inundación.
Electric supply = suministro eléctrico.
Candle = vela.
Motion picture = imágenes en movimiento. Kinetoscope = quinetoscopio.
Phonograph = fonógrafo.
Interactive whiteboard = pizarra digital.
REVIEW - UNIT 6
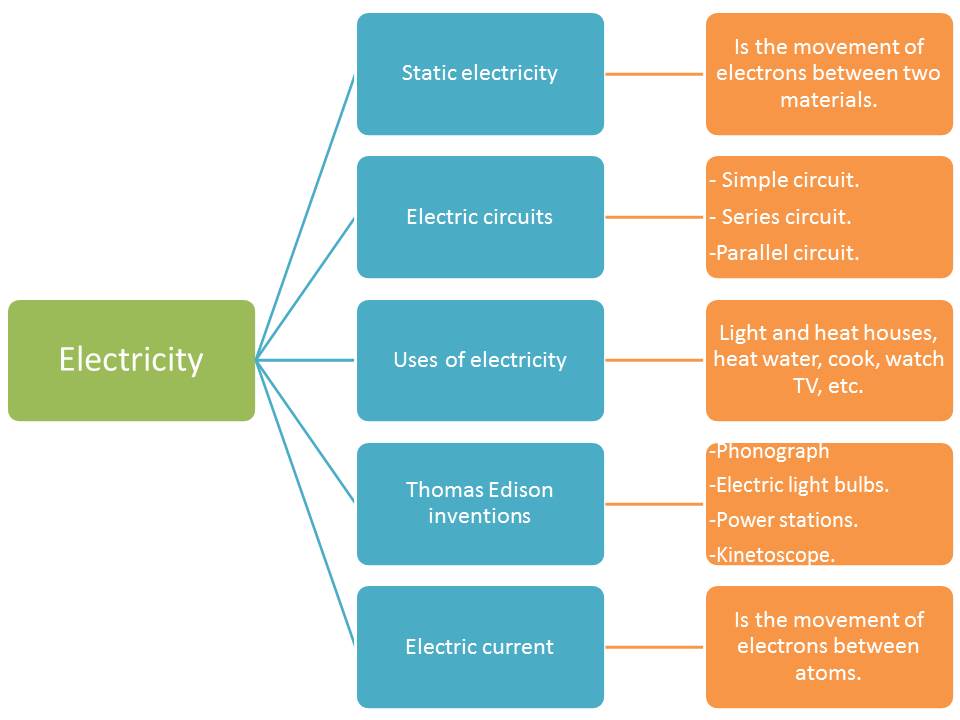
Benjamin Franklin: 1752 - He did a dangerous experiment and discovered that electricity could be controlled.
Electricity: is a form of energy. All matter is made up of microscopic atoms. Electricity is formed when a part of each atom, alled electron, moves from one atom to the other.
Parts of the atom:
- Nucleus: made up of protons (positive charge) and neutrons.
- Electrons (negative charge): revolve around the nucleus.
- Simple circuit: a simple circuit forms a circle. It has a battery, a bulb, a switch and the wire.
- Series circuit: it also formas a circle. It has a battery, two bulbs, a switch and the wire.
- Parallel circuit: forms two or more circles, one bigger that the other. Each circuit has a light bulb.
- Light bulb (1879): he wasn't the first person to invent a light bulb, but he was the first that created one that produced light for a long period of time.
- Kinetoscope (1888): the first motion picture camera.
- Phonograph (1877): a machine that recorded sound.
CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 4 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales Oxford Think Do! Learn 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Money and business (“El dinero y el comercio”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La educación financiera. La definición del dinero y las formas de pago y de ahorro.
- El gasto y el consumo. El consumo responsable.
- Los tipos de presupuestos y la previsión del gasto. Las estrategias de compra.
- La empresa. Los tipos de empresa y actividades empresariales.
- Las formas de organización empresarial. La interpretación de un organigrama.
- La elaboración de pequeños presupuestos personales.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos como las audiciones y canciones de la unidad y la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a contribuir a desarrollar en vuestros hijos unos hábitos de consumo responsable involucrándolos en la planificación del presupuesto familiar semanal. Para ello, pedidles que os ayuden a elaborar la lista de la compra y previsión de necesidades cotidianas analizando los artículos que se suelen consumir y elaborando un presupuesto. Cuando vuestros hijos colaboran en actividades como la compra semanal, se les hace partícipes de la disponibilidad económica y de la necesidad de ajustarse a un plan establecido
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina.
VOCABULARY UNIT 4
UNIDAD 4 – MONEY AND BUSINESS (EL DINERO Y EL COMERCIO)
Ancient = antiguo.
Assistant = ayudante, adjunto.
Bank account = cuenta bancaria.
Banknote = billete.
Bead = cuenta, bolita.
Bond = bono.
Brand = marca.
Budget = presupuesto.
Business = negocio, comercio.
Business budget = presupuesto comercial.
Cargo ship = barco de carga.
Cash = efectivo.
Coin = moneda.
Company = empresa.
Cooperative = cooperativa.
Corporation = compañía.
Cost = gasto.
Credit card = tarjeta de crédito.
Debit card = tarjeta de débito.
Egyptian = Egipcio.
Gold = oro.
Grain = Semilla, grano.
Household bugdet = presupuesto familiar.
Instead of = en lugar de.
Interest = interés.
LISTA DE VOCABULARIO
Manager = director, jefe.
Metal strip = banda magnética.
Mind map = mapa conceptual.
Money box = hucha.
Multinational = multinacional.
National budget = presupuestos del estado.
Organisational chart = organigrama.
Paper notes = billetes.
Partnership = sociedad.
Pocket money = paga.
Retail = venta al por menor.
Salary = salario, sueldo.
Sale = venta.
Salespeople = comercial, vendedor.
Senior employee = directivo.
Share = acción, participación.
Shell = concha.
Sole trader = empresario autónomo.
Spending habits = hábitos de consumo.
Survey = encuesta, estudio.
Tax = impuesto.
To invest = invertir.
To lend = prestar.
To save = ahorrar.
To spend = gastar.
REVISION UNIT 4
MONEY: is any object of value that can be exchanged for a product or service.
HOW CAN WE SAVE MONEY?
- Savings account: people put money into the account and the bank pays interest on it. Interest is a small quantity of money.
- Investing money: you buy something with the objective of selling it later for more money. You can buy shares or bonds.
- Money box: is a box or container where people save money.
- High order products: have a high price and we don't buy them regularly. E.g. a car.
- Low order products: we buy them every week, they have a lower price. E.g. food.
- Household budgets.
- Business budgets.
- Sole trader: a person owns and directs his or her own company.
- Partnership: two or more people own and direct a company together.
- Cooperative: all the people working in the company own together.
- Corporation: is owned by the people who have shares in the company. (If they are very big and in many countries they are called multinacionals).
NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 5


CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 5 de su libro de Ciencias Naturales. Esta unidad tiene por título Heat and Light (“El calor y la luz”), y en ella aprenderá:
- Los fenómenos de naturaleza eléctrica, sus efectos y sus usos. La luz y el calor como fuentes de energía.
- Las propiedades de la luz. Las leyes básicas que rigen los fenómenos: la reflexión y refracción.
- Las características de la luz: la luz blanca y los colores básicos de la luz El comportamiento de los cuerpos ante la luz: cuerpos opacos, transparentes y translúcidos.
- La transformación de la luz en calor. La transmisión del calor: conducción, convención y radiación. Los conductores y los aislantes
- El comportamiento de distintos materiales ante el calor. Los cambios de estado: fusión, evaporación, expansión,y los cambios químicos.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos de las audiciones y canciones de la unidad. Asimismo, os invito a involucrar a vuestros hijos en la tarea de cocinar. Cuando cocinéis, se puede hacer una observación de todo cuanto sucede en la cocina, como si de un laboratorio se tratase: desde el sistema de transmisión del calor de los fogones, el horno, microondas, etc, hasta los efectos del calor en los alimentos. En ocasiones se pueden ver cambios químicos, por ejemplo, cuando un huevo se fríe o se hace una tortilla, un bizcocho, etc.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
VOCABULARIO
Heat = calor.
Light = luz.
Light energy = energía eléctrica.
Electric heater = radiador, calefactor.
Light bulb = bombilla.
Solar panel = panel solar.
CAndle = vela.
Light year = año/luz.
Thermal energy= energía térmica.
Wave= onda.
Computer screen = pantalla de ordenador.
To melt = derretirse.
To travel from = se transmite de.
Conduction= conducción.
Convection= convención.
Radiation = radiación.
Molecule= molécula.
To increase = aumentar.
To rise up = ascender.
To move down = descender.
Electromacnetic waves = ondas electromagnéticas.
Conductor = conductor.
Insulator = aislante.
To transfer = transmitir.
Metal pan = sartén, cazuela de metal.
Substance = sustancia.
Bimetallic strip = lámina bimetálica.
Maize kernels = grano de maiz.
Changes in state = cambios de estado.
Melting = fusión.
Evaporation = vaporización o evaporación.
Expansion = expansión o dilatación.
Chemical changes = cambios químicos.
Physical appearance = aspecto físico.
To vibrate = vibrar.
Oven = horno.
Fairy cakes = magdalenas o bizcocho.
To reverse = revertir.
Radiation = radiación.
Ultraviolet = ultravioleta.
Light phenomena = fenómenos luminosos.
Transparent = transparente.
Translucent = translúcido.
Opaque = opaco.
To block = impedir, obstruir.
Straight line = línea recta.
Shadow = sombra.
Rocky coasts = costas rocosas.
Alluminium foil = papel de aluminio.
Cardboard = cartón.
Cling film = film transparente.
Laws of light = leyes de la luz.
Reflection = reflexión.
Refraction = refracción.
Flickering = parpadear.
twinkling = brillante, centelleante.
To bounce off = rebotar.
Prisms = prismas.
Wrapped = envuelto.
To absorb = absorber.
To vibrate = vibrar.
Periscope = periscopio.
REVIEW UNIT 5
TEMPERATURE: tell us how hot an object is.
HEAT: is the amount of thermal energy that an object has.
LIGHT: is a form of energy that travels through air and space in waves.
HOW DOES THERMAL ENERGY TRAVEL THROUGH OBJECTS?
- CONDUCTION: occurs when two objects are in contact and thermal energy is transferred from one object to the other.
- CONVECTION: occurs when thermal energy travels through a gas or through liquid.
- RADIATION: occurs when thermal energy travels through space by electromagnetic waves.
WHAT IS A THERMAL CONDUCTOR?
It is a material that transfers thermal energy easily.
WHAT IS A THERMAL ISULATOR?
It is a material that doesn’t transfer thermal energy easily.
EFFECTS OF THERMAL ENERGY:
- MELTING: when a solid receives thermal energy, it changes into a liquid.
- EVAPORATION: when thermal energy is applied to a liquid, it changes into a gas.
- EXPANSION: thermal energy causes the molecules in a solid, liquid or gas to vibrate. As a result the material expands.
- CHEMICAL CHANGES: thermal energy can cause chemical changes that are permanent, for example when we cook.
LIGHT PHENOMENA:
Objects react to light in different ways, so we classify them into:
- TRANSPARENT: it doesn’t block the light.
- TRANSLUCENT: it blocks some light, but some light passes through the material.
- OPAQUE: it blocks the light completely.
BASIC LAWS OF LIGHT:
- REFLECTION: causes light to change direction when it hits a surface.
- REFRACTION: causes light to bend as it passes through a substance.
WHITE LIGHT: is made up of all the colours of light together.
HOW IS LIGHT TRANSFORMED INTO HEAT?
When light hits and object, some of the energy is absorbed by the object. This energy makes the object vibrate faster. We feel this vibration as heat.
NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 4

CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 4 de su libro de Ciencias Naturales Oxford Think Do Learn! 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Energy (“La Energía”), y en ella aprenderá:
- Las principales formas de energía y sus características: mecánica, lumínica, sonora, eléctrica, térmica, nuclear y química.
- La transformación de la energía. Su producción y su uso.
- Beneficios y riesgos relacionados con la utilización de la energía: agotamiento, lluvia ácida, radiactividad.
- Las fuentes de energía y las materias primas y el origen del que provienen.
- Las energías renovables y no renovables y sus principales características.
- La utilización de la energía: hábitos de ahorro energético y la conservación del medio ambiente.
Quisiera animaros a hacer un estudio sobre la energía a nuestro alrededor. Con vuestra ayuda, invitad a vuestros hijos a hacer un listado de todo aquello que utilice energía en vuestro entorno durante un día, por ejemplo, lámpara, nevera, tostador, calefacción, coche, panel solar, etc. Cuando tengáis tiempo, sentaros con vuestros hijos y revisar el listado y pensad en cómo podéis tomar medidas de ahorro energético en vuestra vida diaria, por ejemplo, reducir la temperatura de la calefacción, no encender la luz cuando no es necesario y aprovechar la luz natural, caminar en vez de usar el coche, etc.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
VOCABULARIO
Heat = calor.
Wind = viento.
Electricity = electricidad.
Light = luz.
Movement = movimiento.
Wave = ola (oleaje).
Sailing ship = barcos de vela (velero).
To heat up = aumentar la temperatura.
Petrol = gasolina.
Diesel fuel = combustible diésel.
Mechanical energy = energía mecánica.
Chemical energy = energía química.
Thermal energy = energía calorífica o térmica.
Light energy = energía luminosa o lumínica.
Electrical energy = energía eléctrica.
Nuclear energy= energía nuclear.
Vibrations = vibración.
Eardrum = tímpano.
Trolley = carrito.
Kinetic energy = energía cinética.
Potential energy = energía potencial.
To enable = permitir.
Location = ubicación.
Unique = única, distintiva.
Substance = sustancia.
carbohydrate = carbohidrato.
Mobile phone = teléfono móvil.
Battery = batería.
To be stored in = estar almacenado dentro de (algo)...
Heat = calor.
To release = desprender.
To cool down = enfriarse.
Light bulb = bombilla.
Torch = linterna.
Streetlight = farola.
Atomic structure = estructura atómica.
Matter = materia.
To break down = desintegrar.
Radioactive material = material radioactivo.
Uranium = uranio.
Nuclear power station = central nuclear.
LED bulb = bombilla o lámpara LED.
Nail = clavo.
Electrical wire = cable.
Lightning = aparato eléctrico o relampagos.
Sound energy = energía acústica o sonora.
Slice = rebanada.
Slaves = esclavos.
Engine = motor (generador).
Fan = ventilador.
Electric drill = taladro.
Power supply = suministro (Fuente de alimentación).
To power = encender.
Solar panel = panel solar.
Rollercoaster = montaña rusa.
Source of energy = Fuente de energía.
Natural sources = recursos naturales.
Renewable = renovable.
Non-renewable = no renovable.
Petroleum = petroleo.
Coal = carbón.
Hydroelectric power = energía hidroeléctrica.
Wind energy = energía eólica.
Solar energy = energía solar.
Biofuel = biocombustible.
Reservoir = embalse.
Turbine = turbina.
Dam = presa
blade= hélice, hoja.
Biomass = biomasa.
Bioliquid = biolíquido.
Biogas = biogás.
Boiler = caldera.
Natural gas = gas natural.
Underground = subsuelo.
Decayed = en descomposición.
Heating = calefacción.
Coal-burning power station= central térmica convencional de carbon.
Fact-file = ficha.
Tonnes = toneladas.
Acid rain = Lluvia Ácida.
Pollution = contaminación.
Harmful = nocivo.
Carbon dioxide = dióxido de carbono.
Packaging = envoltorio.
To reduce = reducir.
To reuse = reusar.
To recycle = reciclar.
Geothermal energy = energía geotérmica.
REVIEW UNIT 4
ENERGY: is the ability of an object to move, heat up or produce light.
FORMS OF ENERGY:
Mechanical energy: energy that produces movement. E.g. washing machine, kick a ball, push a shopping trolley. 2 types:
- Kinetic energy: is energy in the form of movement.
- Potential energy: is energy in the form of potential movement.
Chemical energy: is stored in some substances. E.g. Carbohydrates in pasta.
Thermal energy: is energy in the form of heat. E.g. Cook food.
Light energy: is energy in the form of light. E.g. Light bulbs.
Electrical energy: is energy in the form of electricity. E.g. Television.
Nuclear energy: this type of energy is stored in atomic structure of all matter. Scientist create energy by breaking down radioactive materials. E.g. Uranium.
SOURCES OF ENERGY:
Renewable energy sources:
- Hydroelectric energy: we get hydroelectric energy from water that is moving or falling.
- Wind energy: we get wind energy from the movement of air.
- Solar energy: we get solar energy from the Sun in the form of light and heat.
- Biofuels: we get biofuels from plan and animal products.
Non-renewable energy sources:
- Petroleum: black liquid that is formed underground from decayed plants and animals.
- Coal: black rock composed mainly of carbon.
- Natural gas: mixture of gases that have formed from decayed living organisms.
- Uranium: radioactive metal found in rocks.
Problems of non-renewable energy sources:
- Resources are limited.
- Pollution.
- Global warming.
- Acid rain.
The three Rs:
- Reduce.
- Reuse.
- Recycle.
SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 3

CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 3 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales Oxford Think Do! Learn 5. Esta unidad tiene por título The tertiary sector (“El sector terciario”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La identificación del tercer sector de la economía y la clasificación de las actividades económicas relacionadas con él.
- El sector servicios: el transporte de pasajeros y de mercancías y el turismo.
- El comercio: la venta al por menor y tipos de negocios.
- Los tres sectores de la economía en España y la Unión Europea.
- La función y las técnicas publicitarias más habituales. El juicio crítico de la publicidad y el consumo responsable.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos y la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a reflexionar acerca de la publicidad y los efectos que produce en el consumidor. Es conveniente que ayudemos a nuestros hijos a tener una actitud responsable ante el consumismo y analizar las técnicas que utiliza la publicidad para captar al consumidor. Conviene que les expliquemos que muchas veces la publicidad no es totalmente objetiva y puede inducirnos a comprar compulsivamente productos que no son necesarios o que realmente no ofrecen lo que puede parecer a simple vista.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
VOCABULARIO
The tertiary sector (El sector terciario) Unidad 3
advertise = anunciar, promocionar
advertisement = publicidad, anuncio
air transport = transporte aéreo
bank clerk = empleado de banco
business = negocio
cargo ship = barco de carga
civil servant = funcionario
compete = competir
concert hall = auditorio
consumption = consumo
cruise ships = barco de crucero
currency = moneda, divisa
customer = cliente
department stores = grandes almacenes
economic links = relaciones comerciales
electrician = electricista
encourage = animar
health sector = sanidad
hypermarket = hipermercado
judge = juez
judicial system = el sistema judicial
lawyer = abogado
load = carga
organic/eco-friendly product = productos ecológicos
passenger = pasajero
payment = pago
prosecutor = fiscal
public safety = seguridad ciudadana
rail transport = transporte ferroviario
retail = venta al por menor
road transport = transporte terrestre
sale = venta
security guard = vigilante de seguridad
skilled job = trabajo especializado
speciality shop = tienda especializada
sports stadium = estadio o palacio de los deportes
tanker = buque
target market = mercado meta
tertiary sector = el sector terciario
tourism = turismo
trade = comercio
trainers = zapatillas de deporte
transport links = redes de transporte
unload = descargar
washing powder = detergente en polvo
water transport = transporte marítimo
REVIEW UNIT 3
Tertiary sector: consists of activities that provide a service. E.g. transport, communications, etc.
We can divide services in:
|
AREAS |
JOBS |
|
Health |
Doctors, nurses and dentists. |
|
Education |
Teachers |
|
Public safety |
Police officers, firefighters, soldiers and security guards. |
|
Skill jobs |
Mechanics and electricians. |
|
Administrative |
Secretaries, bank clerks and civil servants. |
|
Cultural professions |
Writers, musicians, actors, painters and sculptors. |
|
Judicial system |
Lawyers, prosecutors and judges. |
Transport industry: moves passengers and products from one place to another. Classification:
- Water transports: cruise ships, cargo ships and tankers.
- Rail transports: trains.
- Road transports: cars, buses and lorries.
- Air transports: planes.
Tourism industry: provides accommodation and entertainment for tourists. Classification:
- Beach tourism.
- Cultural tourism.
- Rural tourism.
- Adventure tourism.
Spain is one of the most popular destinations, because of the climate, culture, beaches and monuments.
Retail: is the selling of products to consumers. Types:
- Hypermarkets: very large supermarkets.
- Supermarkets and department stores: large businesses that sell a variety of different products:
- Speciality shops: smaller businesses that offer only one type of product or service.
Advertisements: tells consumers about a product or a service. They also encourage people to buy that product or service. They can be advertised on:
- Television.
- Internet.
- Magazines.
- Newspapers.
Tertiary sector in the EU:
- It is the largest sector.
- There’s a lot of trade between EU countries because of transport and economic links.
- Time differences are small so it is easier for companies to do businesses.
SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 2

CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a está estudiando la unidad 2 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales Oxford Think Do! Learn 5. Esta unidad tiene por título The economy (“La economía”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La economía y las actividades económicas y productivas.
- La identificación de las actividades de cada sector.
- Los sectores de la producción: el sector primario. La agricultura, la ganadería y la pesca.
- La minería y la exploración forestal.
- La identificación de las materias primas y los productos elaborados.
- El sector secundario: los sectores de la producción. La identificación de los bienes de equipo y los bienes de consumo.
- El proceso de obtención de los productos.
- Los sectores de la producción en España.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando wela las actividades de Let’s play! ubicados en la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a pensar en las personas que pertenecen a vuestras familias o a vuestro entorno más inmediato y analizar en qué consiste su labor y función en sus distintos empleos. Después, intentar clasificar sus profesiones en los distintos sectores de la actividad productiva.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina.
VOCABULARIO:
The economy (La economía)
agriculture = la agricultura
arable farming = agricultura
auction = subasta
bark = corteza
cellulose = celulosa
coastal area = zonas/franja costera
coastal fishing = pesca de bajura o litoral
cork = corcho.
crops = cultivos, cosecha
deep-sea fishing = pesca de altura
dry farming = de secano
economy = economía
extensive farming = ganadería extensive
factory = fábrica
field = campo
fishing = la pesca
forestry = forestal
forestry = la silvicultura o explotación forestal
furniture = muebles
granite = granito
intensive farming = ganadería intensiva
irrigated farming = de regadío
lipstick = lápiz de labios
livestock = ganado
manufacture = elaborar
manufactured products = productos elaborados
marble = mármol
mining = la minería
opencast mines = minas a cielo abierto
pasture = pastos
pens = corrales
pits = pozos
poison = envenenar
primary sector = el sector primario
quarries = canteras
raw materials = materias primas
resin = resina
resources = recursos
secondary sector = el sector secundario
sector of the economy = sectores productivos
services = servicios
shafts = pozos
slate = pizarra
stable = establo
tertiary sector = el sector terciario
throw away = desechar
tourism = turismo
transportation = transporte
underground mines = mina subterránea
water supplies = reservas acuíferas
workshop = taller
chemical industry = industria química
intermediate products = bienes de equipo
consumer products = bienes de consumo
steel industry = siderurgia
steel = acero
sources = fuentes
limestone = caliza
silica = sílice
copper = cobre
REVIEW UNIT 2
Economy: the system of using resources, buying and selling.
Raw materials: products from nature.
PRIMARY SECTOR: provides raw materials from nature. It includes: agriculture, fishing, mining and forestry.
Agriculture: is the cultivation of crops and the raising of livestock.
- Arable farming: produces crops for food and other products. There are two types:
|
Dry farming |
Irrigated farming |
|
Farmers don’t water their crops. Large fields. e.g. Wheat, grapes, crops. |
Farmers use irrigation systems to water their crops. Small fields. e.g. Tomatoes, beans and melons. |
- Livestock farming: is the raising of animals for food and non-food products. There are two types:
|
Extensive farming |
Intensive farming |
|
Farmers raise their livestock in large fields. Animals eat from the land. e.g. Iberian pigs. |
Farmers raise their livestock in stables. Farmers give food to the animals. e.g. Milk cows. |
Fishing: There are two types:
|
Coastal fishing |
Deep-see fishing |
|
Near the coast. They use small boats and traditional methods. |
Is far from the coast. They spend weeks even months on large ships.
|
Mining: is the extraction of rocks and minerals from the ground. There are two types of mines: underground mines and quarries.
Forestry: is the use of forest to obtain plant products. e.g. cork.
SECONDARY SECTOR: processes raw materials and provides manufactured products. There are two types of products:
- Intermediate products: these products are used by other industries. e.g. Steel.
- Consumer products: these products are sold directly to consumers. e.g. Car
TERTIARY SECTOR: provides a variety of services.
ENERGY SOURCES: are used in industries to transform raw materials into manufactured products. There are two types of sources:
- Renewable sources:they are unlimited. e.g. sunlight, water or wind.
- Non-renewable sources:they are limited. e.g. coal, oil, natural gas or nuclear energy.
GEOGRAPHY OF SPAIN
SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 1
CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 1 de su libro de Ciencias Sociales Oxford Think Do! Learn 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Population (“La población”), y en ella aprenderá:
- El fenómeno de la población y sus conceptos básicos: demografía, natalidad, mortalidad y la densidad de población. Su distribución en grupos y evolución.
- Los movimientos migratorios.
- La interpretación de los distintos gráficos para el estudio de la población: gráfica lineal, diagrama de barras, gráfica de sectores y pirámides de población.
- El estudio del mapa de la población en España y Europa.
- La densidad de población y distribución núcleos de población de España y Europa.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando las audiciones de la unidad, la presentación powerpoint y las actividades de Let’s play! ubicados la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a buscar en periódicos, revistas o con la ayuda de Internet algunos gráficos relacionados con la inmigración o el desempleo en España y posteriormente interpretar y comentar con vuestros hijos.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina.
LISTA DE VOCABULARIO
Population (La población) Unidad 1
age = edad
age group = grupo de edad
average number = promedio
bar chart = gráfico de barras
birth = nacimiento
blond-haired = rubio/a
Buddhist = budista
Christian = cristiano
coastal area = zonas/franja costera
dark-haired = moreno/a
death = muerte
decrease = descender, disminuir
demography = demografía
emigrant = emigrante
ethnic group = grupo étnico
female = mujer
fertility rate = tasa de natalidad
fewer = menos
gender = género
graph = gráfico
grow = crecer, aumentar
growth = crecimiento
increase = aumentar
immigrant = inmmigrante
line graph = gráfica lineal
male = hombre/varón
migration = migración
municipality = municipio
Muslim = musulmán
nationality = nacionalidad
percentage = porcentaje
pie chart = gráfica de sectores
population = la población
poverty = pobreza
pyramid graph = pirámide (de población)
research = investigación
retired = jubilado
square kilometre = kilómetro cuadrado
unemployment = desempleo
war = guerra
REVIEW UNIT 1
DEFINITIONS:
Demography: is the study of population.
Population density: the number of people living in each square kilometer.
Fertility rate: is the average number of children per family.
Migration: is the movement of people from one area to another.
Immigrants: people that live and work in one country, but are from another country.
Emigrants: people that leave their country to live in a different one.
QUESTIONS:
What is the population of the world?
The population of the world is more than 7 billon people.
Why does population change?
Because people are born or die every minute and people move around to find work or scape natural disasters and wars.
How can we divide a population?
We can divide the population in groups, according to various factors, such as gender, age, ethnic or religion.
How is the population of Spain?
Population has increased during the past century especially from 2000 to 2011, as a result of immigration. In 2012, the population started to decrease as immigrants returned home because of high unemployment.
SPAIN:
|
Population |
46.7 million |
|
Population density |
91 per km2 |
|
Fertility rate |
1.47 children per family |
EUROPE:
|
Population |
730 million |
|
Population density |
114 per km2 |
|
Fertility rate |
1.6 children per family |
GRAPHS AND CHARTS

NATURAL SCIENCE UNIT 3



CARTA A LOS PADRES
Unidad 3
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 3 de su libro de Ciencias de la Naturaleza Oxford Think Do Learn! 5. Esta unidad tiene por título Ecosystems (“Los ecosistemas”), y en ella aprenderá:
- Las características y componentes un ecosistema.
- Los ecosistemas más importantes y su clasificación: pradera, charca, bosque, litoral y ciudad.
- Los seres vivos que habitan en un ecosistema y relaciones entre ellos y su hábitat.
- Las relaciones tróficas y las cadenas y redes alimentarias. Descripción de su funcionamiento.
- La bioesfera.
- Los cambios en los ecosistemas. Causas y consecuencias.
- Las consecuencias de la actividad humana: contaminación, deforestación, desertización, etc…).
- La investigación de los ecosistemas y la contaminación.
- La protección del medio ambiente.
Quisiera animaros a elaborar un “decálogo” de compromisos para ayudar a proteger el medio ambiente. Podéis acordar entre todos los miembros de la familia unos compromisos fáciles de llevar a cabo (ahorrar energía aparando las luces cuando no son necesarias, recogida selectiva de basura, etc…) y ponerlos por escrito en una cartulina que se debe de colocar en un lugar visible, como la cocina, para poder revisar a menudo.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
LISTA DE VOCABULARIO
Ecosystem = ecosistema.
Habitat = hábitat.
Tropical rainforest = selva tropical.
To become extinct = extinguirse.
Climate = clima.
Biotope = biotopo (medio físico).
Biocoenosis = biocenosis.
Relief = relieve.
Population = población.
Community = comunidad.
Intraspecific relationships = relaciones intraespecíficas.
Interspecific relationships = relaciones interespecíficas.
Trophic relationships = relaciones tróficas.
Producer = productor.
Primary consumers = consumidores primarios.
Secondary consumers = consumidores secundarios.
Terciary consumers = consumidores terciarios.
Decomposers = descomponedores.
Food chain = cadena alimentaria.
Remains = restos.
Praying mantis = mantis religiosa.
Pond = charca.
Woodland = bosque.
Coast = litoral.
Prairie = llanuras.
City ecosystem = ecosistema urbano.
Biosphere = la bioesfera.
Habitat = hábitat.
biome = bioma.
Environmental conditions = condiciones medioambiantales.
Pollution = contaminación o polución.
Over-fishing = sobrepesca.
Forest fires = incendios forestales.
Deforestation = deforestación.
REVIEW UNIT 3
Ecosystem: includes all of the living and non-living things in a particular place and the relationships between them.
It is made up of two parts:
1. Biotope: non-living things in an ecosystem (temperature, soil, light, …)
2. Biocoenosis: living things in an ecosystem (plants, animals, …)
Relationships of an ecosystem:
1. Intraspecific relationships: between individual members of the same species.
2. Interspecific relationship: between individual members of different species.
Population: is a group of organisms that live together and belong to the same species.
Community: is a collection of different populations that live together in one place.
Trophic relationships: the relationships between the organisms that eat and the organisms that are eaten.
1. Producers (plants): make their own food.
2. Primary consumers (herbivores): they feed on plants.
3. Secondary consumers (carnivores): they feed on herbivores.
4. Tertiary consumers (carnivores): they feed on secondary consumers.
5. Decomposers (fungi and bacteria): they break down the remains of dead organisms.
Food chain: shows the trophic relationships between different organisms.
|
|
CHARACTERISTICS |
LIVING THINGS |
NON-LIVING THINGS |
|
POND |
Small areas of water and land. |
Aquatic plants, ducks, turtles. |
Water, soil and sand. |
|
WOODLAND |
Can be flat or hilly. Sometimes can have mountains and valleys. |
Trees, snakes, squirrels. |
Soil, rocks, rivers. |
|
COAST |
Areas with sea, beaches, cliffs, dunes or rock pools. |
Seaweed, fish, starfish. |
Water, rocks, sand. |
|
PRAIRIE |
Large, flat areas. |
Grasses, zebras, rabbits. |
Soil, rivers and lakes. |
|
CITY |
Can be flat, hilly, with rivers or lakes, or on the coast. |
Grasses, bushes, pigeons, insects. |
Buildings, roads |
Habitat: is the place where a particular living thing lives. There can be many habitats in an ecosystem. Sometimes living things can share a habitat.
Biome: an ecosystem that has several types of habitat.
Biosphere: is all the ecosystems on the Earth. It includes the oceans, the land and the atmosphere, and all living things on the planet.
What causes natural changes?
1. Seasonal changes.
2. Natural development of ecological communities.
What consequences does human activity have?
1. Pollution.
2. Overfishing.
3. Forest fires.
4. Deforestation.
NATURAL SCIENCE - UNIT 2

CARTA A LOS PADRES
Estimados padres o tutores:
Vuestro hijo/a va a comenzar la unidad 2 de su libro de Ciencias de la Naturaleza Oxford Think Do Learn! 5. Esta unidad tiene por título The classification of living things (“La clasificación de los seres vivos”), y en ella aprenderá:
- La clasificación de los seres vivos en reinos: el reino animal, el reino de las plantas, el reino hongos, el reino protistas y el reino moneras.
- Los distintos grupos de animales vertebrados y sus características.
- La alimentación, respiración y reproducción de los vertebrados.
- Los distintos grupos de animales invertebrados y sus características.
- La alimentación, respiración y reproducción de los invertebrados.
- La clasificación y características de las plantas.
- Las características y descripción de los seres vivos del reino hongos, moneras y protistas. Sus funciones vitales.
- El estudio y observación de los seres vivos con instrumentos, medios y criterios científicos adecuados.
Os adjunto el vocabulario más importante que aprenderá a lo largo de la unidad.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos como las audiciones y canciones de la unidad, la presentación powerpoint y la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a realizar una práctica de observación con vuestros hijos: dad un paseo por una zona protegida o parque natural cercano a vuestros domicilios. Observad y describir los seres vivos que encontréis: aves, mamíferos, reptiles, insectos, hongos, plantas, etc, y comentad sus características.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina
LISTA DE VOCABULARIO
Aerodynamic body = cuerpo aerodinámico.
Alga (pl. “ae”) = alga(s).
Amoebae (pl. “amoebas”) = ameba(s).
Amphibian = anfibios.
Angiosperms = angiospermas.
Animal kingdom = reino animal.
Annelids = anélidos.
Aquatic mammals = mammíferos acuáticos.
Arthropods = artrópodos.
Autotrophs = autótrofos.
Birds = aves.
Bud = brote.
Ciliates = ciliados o cilióforos.
Cillium (pl. -a) = cilio(s).
Coelenterates = celentéreos.
Cones = cono o piña.
Conifers = coníferas.
Crustaceans = crustáceos.
Echinoderms = equinodermos.
Edible = comestible.
Exoskeleton = exoesqueleto.
Ferns = helechos.
Fish = pez.
Flagellates = flagelados o mastigóforos.
Fronds = frondes.
Fungi kingdom = reino hongos.
Gymnosperms = gimnospermas.
Hard shell = concha.
Heterotrophs = heterótrofos.
Hypha(pl.”ae”) = hifa(s).
Kingdom = reino.
Lead = plomo.
limbs = extremidades o miembros.
Malaria = la malaria.
Molluscs = moluscos.
Monera kingdom = reino monera.
Mosses = musgos.
mould = moho.
Non-see plants = plantas sin semillas.
Nuts = frutos secos
Oviparous = ovíparo.
Paramecium (pl. –cia) = paramecio(s).
Plant kingdom = reino de las plantas.
Poisonous = tóxico.
Pores = poros.
Porifera = poríferos (esponjas).
Powder = polvo.
Protective covering = cubierta protectora.
Protista kingdom = reino protoctistas.
Protozoan (pl. “protozoa”) = protozoo(s).
Pseudopods = seudópodo.
Reptiles = reptiles.
Rizhoids = rizomas.
Spiders = arácnidos.
Spinal column = columna vertebral.
Spinal cord = médula espinal.
Spores = esporas.
Sporozoa = esporozoos.
Tentacles = tentáculos.
Terrestrial mammals = mamíferos terrestres.
To pollute: contaminar.
Truffles = trufas.
Viviparous = vivíparo.
REVISION UNIT 2
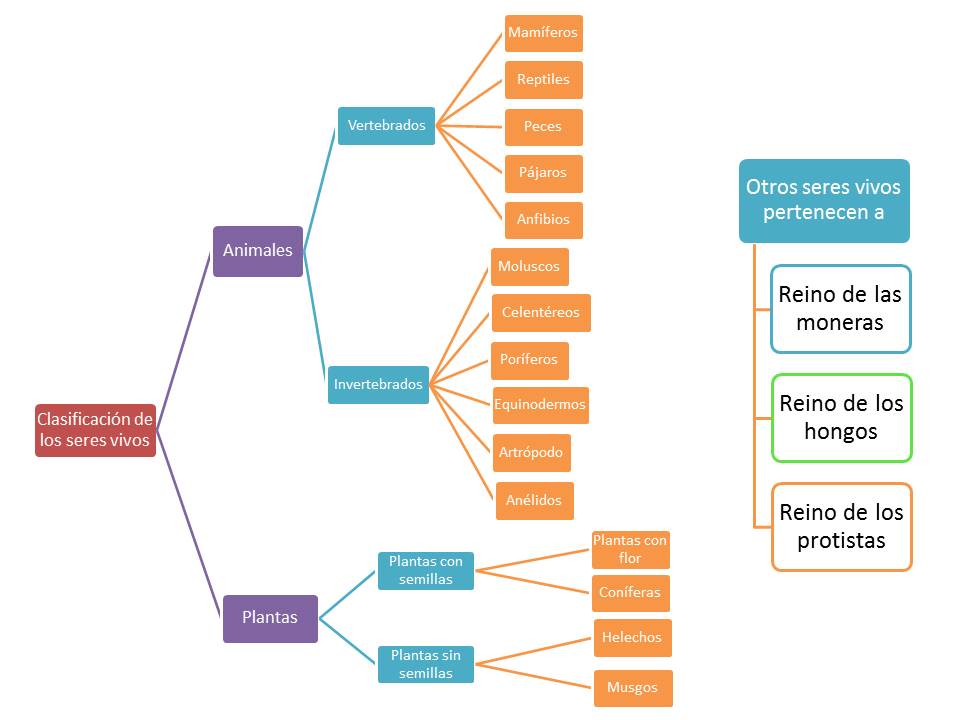
Living things are divided into five kingdoms:
- Animals kingdom.
- Plant kingdom.
- Monera kingdom.
- Protista kingdom.
- Fungi kingdom.
|
VERTEBRATES |
||||
|
|
Bodies |
Extremities |
Respiration |
Reproduction |
|
MAMMALS |
They have skin, hair and fur. |
4 legs (humans 2 legs and 2 arms and dolphins 2 fins) |
With lungs. |
Viviparous. |
|
REPTILS |
They have scales. Some have shells. |
Many have 4 legs. Some don’t have legs (snakes) |
With lungs. |
Oviparous. |
|
FISH |
They have scales. |
Have fins and tails. |
With gills. |
Oviparous. |
|
BIRDS |
Have aerodynamic bodies. Thin and light bones. |
Two legs and two wings. |
With lungs. |
Oviparous. |
|
AMPHIBIANS |
Thin, smooth skin. |
4 legs (sometimes they have a tail) |
With gills and lungs. |
Oviparous. |
|
INVERTEBRATES |
|||
|
|
MOLLUSCS |
COELENTERATES |
PORIFERA |
|
Respiration |
Gills. |
Skin. |
Pores. |
|
Reproduction |
Oviparous. |
Buds. |
Buds. |
|
Body |
Soft body. Hard Shell (some animals) |
Soft body. |
Soft body. Pores. |
|
Extremities |
---------------- |
Tentacles. |
-------------- |
|
INVERTEBRATES |
|||
|
|
ECHINODERMS |
ARTHROPODS |
ANNELIDS |
|
Respiration |
Gills. Skin. |
Lungs. Gills. |
Skin. Gills. |
|
Reproduction |
Oviparous |
Oviparous. |
Oviparous. Buds. |
|
Body |
Sharp spikes. |
Exoskeleton. |
Long and soft body that is divided in segments. |
|
Extremities |
Tentacles. |
Legs. |
---------------- |
|
VERTEBRATES AND INVERTEBRATES EXAMPLES |
|
|
Mammal |
Pig |
|
Reptiles |
Snake |
|
Fish |
Bonito |
|
Bird |
Chicken |
|
Amphibian |
Frog |
|
Mollusc |
Snail |
|
Coelenterates |
Jellyfish |
|
Porifera |
Sponge |
|
Echinoderms |
Starfish |
|
Arthropods |
Spider |
|
Annelids |
Worms |

FUNGI, MONERA AND PROTISTA KINGDOMS:
|
FUNGI, MONERAN AND PROTISTA |
||||
|
|
REPRODUCTION |
NUTRITION |
BODY/SHAPE |
MOVEMENT |
|
FUNGI |
Spores. |
Absorb nutrients from the decaying matter. |
Unicellular or multicellular. |
_____________ |
|
MONERAN |
Dividing cells. |
Some absorb nutrients from the decaying matter, others create their own food. |
Unicellular.
Different shapes. |
Some have tail to move. |
|
PROTISTA |
Spores or dividing cells. |
Some carry out photosynthesis to produce food. Others eat matter. |
Unicellular or Multicellular. |
Some don’t move. Other move in different ways. |
Natural Science - UNIT 1

UNIT 1 CONTENTS AND VOCABULARY
Dear families and pupils,
this is what we're studying in unit 1!
Queridas familias y alumnos,
esto es lo que estamos estudiando en la unidad 1!
- Las tres funciones vitales básicas de los seres vivos: relación, nutrición y reproducción.
- La estructura interna de los seres vivos: tipos de células y sus partes, tejidos, órganos, aparatos y sistemas. Las características y funciones de los mismos.
- La distinción entre organismos unicelulares y pluricelulares.
- La estructura de un organismo pluricelular animal y vegetal y las funciones de sus partes.
- Los sistemas de organismo de los animales y del cuerpo humano y sus funciones.
- La descripción de las células, tejidos y órganos del aparato respiratorio.
- La función vital de un organismo unicelular: la levadura.
Quisiera animaros a que ayudéis a vuestro hijo/a a interiorizar los contenidos utilizando los recursos de la unidad y la Plus Zone. Asimismo, os invito a realizar una práctica de observación con vuestros hijos: dejad un producto lácteo abierto durante unos días hasta que comience a formarse moho en él. Id observando el avance y crecimiento del mismo y valoradlo con vuestros hijos al fin de la unidad para percibir cómo funciona el proceso de nutrición de los seres unicelulares como el moho.
Sin duda, vuestra colaboración ayudará a que vuestro hijo/a aprenda y se divierta.
Saludos,
Cristina.
VOCABULARIO
Biodiversity = biodiversidad.
Species = especie.
Fungus = hongo.
Cell = célula.
Spherical = esférico.
Tubular = tubular.
Spiral=espiral.
Nucleus = núcleo.
Cytoplasm = citoplasma.
Membrane = membrana.
Organelles: orgánulos.
Chloroplast = cloroplasto.
Chlorophyll = clorofila.
Vacuole = vacuola.
Unicellular = unicelular.
Multicellular = pluricelular.
Yeast = levadura.
Tissue = tejido.
System = sistema o aparato.
Organ = órgano.
Lymph = linfa.
Fibrous = fibroso.
Red blood cell = células sanguíneas.
Nerve cells = células nerviosas.
Reproductive cells = células sexuales.
Sap = savia.
Chlorophyll = clorofila.
Photosynthesis = fotosíntesis.
Digestive system = aparato digestivo.
Respiratory system = aparato respiratorio.
Circulatory system = aparato circulatorio.
Muscular system = sistema muscular/la musculatura.
Skeletal system = sistema óseo/el esqueleto.
Nervous system = sistema nervioso.
Sense organs = órganos de los sentidos.
Male reproductive system = aparato reproductor masculino.
Female reproductive system = aparato reproductor femenino.
Foetus = feto.
Embryo = embrión.
Uterus = útero.
Respiratory epithellum cells = células epiteliales.
REVISION UNIT 1
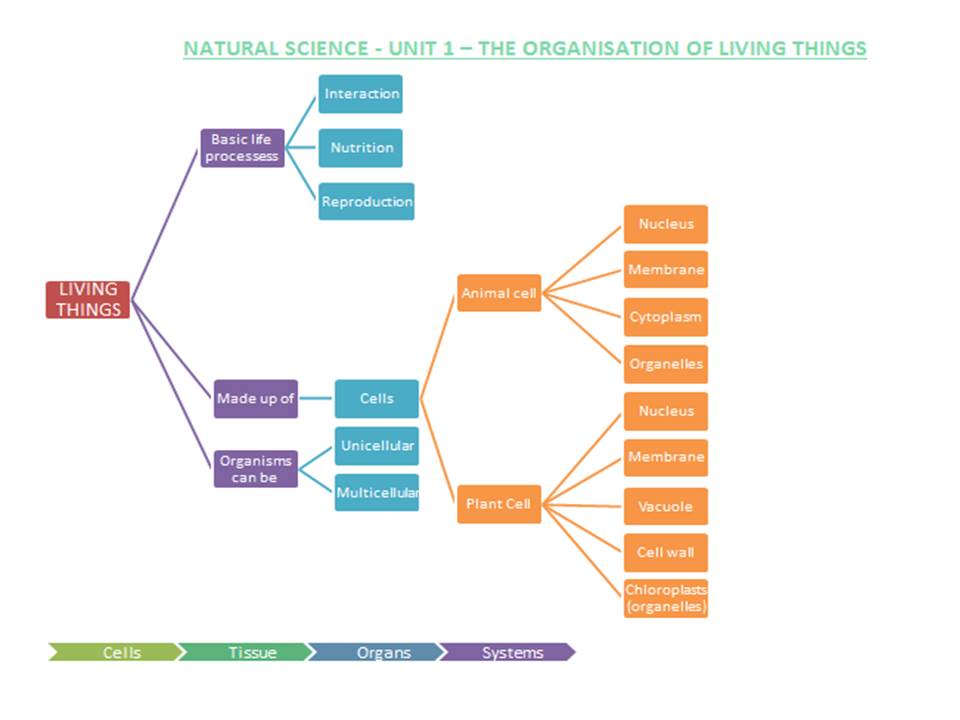
BASIC LIFE PROCESSES:
Interaction: is the process of reacting to things in the environment.
Nutrition: is the process of taking in food and liquids.
Reproduction: is the process of creating new members.
ANIMAL CELL: (the shape can be spiral, spherical, tubular and star-shaped; depending on the function)
Nucleus: controls everything that happens inside the cell.
Membrane: surrounds and protects the cell.
Cytoplasm: is a thick, clear liquid protected by the membrane.
Organelles: carry out different life processes.
PLANT CELL: (they can be rectangular and polygonal)
Nucleus
Membrane
Cell wall: it is around the membranes, this helps support the plant.
Vacuole: it is like a bag. Food and water are store in it.
Chloroplasts: they are organelles. They contain green liquid called chlorophyll.
MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS:
They have two or more cells.
UNICELLULAR ORGANISMS:
They only have one cell.
THREE EXAMPLES OF CELLS:
Red blood cells, nerve cells and reproductive cells.
ANIMALS AND PLANTS ORGANISATION:
Systems are made up of organs.
Organs are made up of tissue.
Tissue is made up of cells.
FUNCTION OF THE ROOTS: absorb nutrients and water from the soil.
FUNCTION OF STEMS: support the plant and transport water, minerals and sap throughout the plant.
SYSTEMS INVOLVED IN THE LIFE PROCESSES:
Nutrition: digestive system, respiratory system and circulatory system.
Interaction: muscular system, skeletal system and nervous system.
Reproduction: female reproductive system and male reproductive system.
.jpg?ph=f6c3739523)